
Next week – August 2nd to be precise – marks Earth Overshoot Day, 2023. The date of this “holiday” changes every year to reflect the point at which humanity’s consumption of ecological resources exceeds what Earth can regenerate in that year. In other words, by next Wednesday, we’ll have used up all of 2023’s resource allotment if we want to remain in equilibrium. All resources consumed after that date will be overshooting that equilibrium.
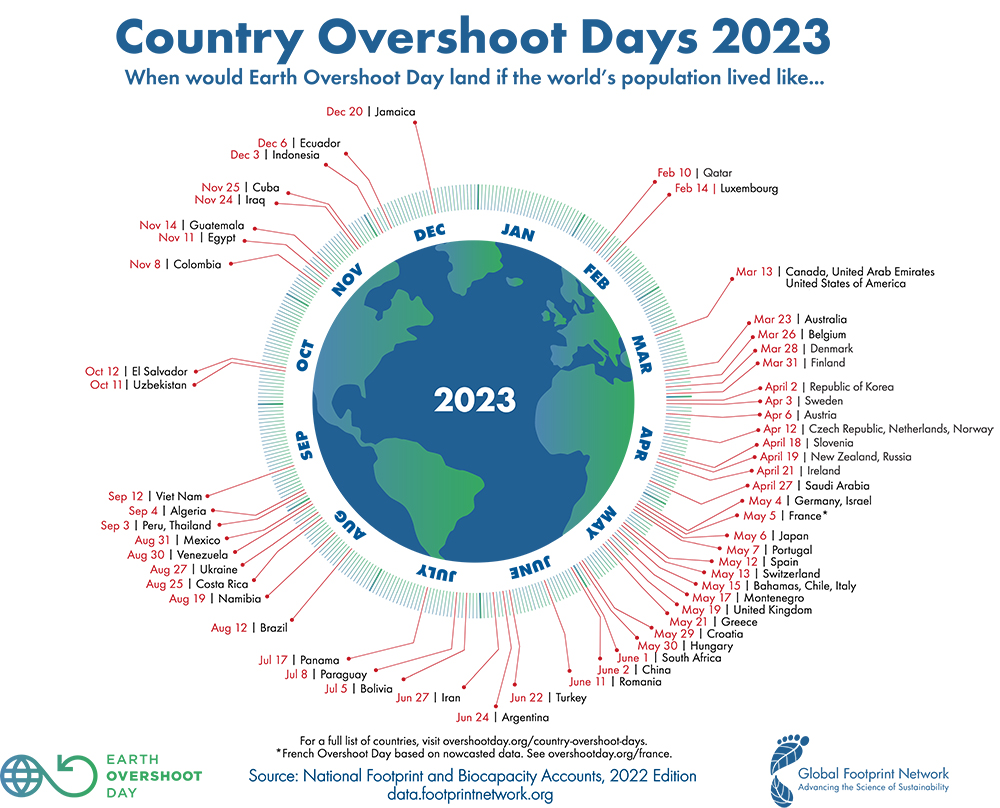
Graphic by the Global Footprint Network.
As the world grapples with the reality of diminishing resources and increasing global temperatures, time to reduce humanity’s ecological footprint is running out. One of 2023’s trendiest technologies may just hold the key to developing innovative solutions – if we can overcome the obstacle of its ecological footprint…
We’re talking of course about artificial intelligence (AI); specifically, climate AI’s capacity to supercharge climate tech innovation, as well as its resource-intensive development.
The growing intersection between AI and climate change presents enormous opportunities for both fields. As generative AI applications become more sophisticated, they can provide invaluable insights into climate change’s complex dynamics and help identify effective strategies for mitigation and adaptation. Simultaneously, the urgent need to address climate change serves as an ideal testing ground for further development and refinement of AI technologies. The progress made in this domain will undeniably shape the way humanity approaches the challenge of preserving the planet for future generations.
Let’s take a closer look.
Generative AI Applications
Since ChatGPT came onto the scene and rocked the tech world, we would be remiss if we didn’t mention the role of generative AI in the fight against climate change.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms and deep learning techniques, scientists can analyze vast amounts of data, uncover patterns, and make predictions about future climate trends. These applications can significantly contribute to both understanding and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Simulating Scenarios for Climate Science
One major area for generative AI applications is climate science. Researchers use advanced models to simulate and predict various climate scenarios, allowing them to better understand the potential consequences of different emission levels. For example, climate AI research and modeling can help identify the most effective ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By analyzing historical data, AI-powered models can predict the impacts of policy changes on emissions and suggest the most effective measures to implement.
Natural Disaster Risk Management
AI has also shown promise in managing and mitigating risks related to natural disasters. Accurate predictions of extreme weather events and pattern analysis allow experts to better prepare and respond to natural disasters. These insights help to minimize the damage caused by these events and inform decision-makers on the necessary steps to ensure public safety.
AI in Energy Management
Lastly, generative AI is instrumental in the energy sector, where machine learning algorithms can optimize electricity usage. For example, Gridmatic uses generative AI to model the US electricity grid down to the nodal level. This model allows the Cupertino-based startup to:
- Forecast demand,
- Predicting solar and wind output based on weather data,
- Manage power distribution and transmission,
- Predicting energy market prices,
- Identify customer usage patterns,
- And optimize energy storage.
By learning the patterns of energy consumption, AI can contribute to more efficient use of resources and lower emissions. This is particularly important in the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which require efficient management to fully harness their potential.
4 Top Climate AI Startups
Of course, AI describes a much broader field than just generative AI applications. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data, predict patterns, and optimize resource use has made it an indispensable tool in the quest to understand and mitigate the effects of this global crisis.
Here are 5 of the most exciting startups leveraging climate AI to innovate solutions to our climate crisis.

1. BrainBox: Reducing Carbon Emissions
AI can significantly contribute to reducing carbon emissions by optimizing various processes in key sectors. For instance, AI plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Startups like Montreal-based BrainBox AI are implementing AI-driven solutions that can potentially reduce a building’s carbon footprint by 20% to 40%.
Furthermore, AI can assist in measuring emissions more accurately at both macro and micro levels. Better data collection and analysis can help policymakers and businesses make more informed decisions about emissions reduction strategies.

2. Descartes: Building Climate Resilience
As the climate crisis intensifies, resilience and adaptation become more important. AI can help us build climate resilience by forecasting climate-related risks and informing necessary safeguards. Descartes’ SaaS platform powers the analysis of geospatial data at scale. Such data can help governments and organizations:
- Predict the impact of extreme weather events, enabling governments and organizations to prepare more effectively.
- Optimize agricultural practices to account for changing climate patterns, thereby ensuring sustainable food production.
- Increase efficiency and reduce resource consumption in mining and manufacturing.

3. AgroScout: AI in Agriculture
Agriculture is one of the leading contributors to climate change. That’s why startups like AgroScout are leveraging AI technologies to transform the agricultural sector by optimizing resource usage and promoting sustainable practices. The company’s SaaS platform analyzes data from satellite images, sensors, and drones to monitor soil health, predict weather patterns, and streamline irrigation systems. This data-driven approach not only improves crop yields but also reduces the environmental impact of farming practices. AI-powered tools also aid in the early detection and management of pests and diseases, enhancing overall agricultural resilience.

4. Unravel Carbon: AI in Carbon Capture
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) before it’s released into the atmosphere.
Startup Unravel recognized that some of the largest contributors to emissions (i.e. large corporations) are also the most potent agents for change. So they developed an innovative platform that can quickly convert a company’s accounting data into comprehensive supply chain carbon data, offering detailed emission analytics and generating relevant AI and climate change solutions automatically.
Other applications for AI in this field aim to enhance carbon capture techniques, such as direct air capture systems, by optimizing their performance through real-time data analysis. These innovations are vital in the race to achieve net-zero emissions.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Climate Change
Energy Efficiency of AI Technologies
As noted, the greatest challenge in leveraging climate AI is the ecological footprint of AI itself. The increased use of AI has led to an escalation in energy demand from data centers, which contributes to a considerable carbon footprint.
To put this into perspective, training ChatGPT’s GPT3 model produced 500 metric tons of CO2 – the equivalent of a gasoline-powered car driving over a million miles. Meanwhile, researchers estimate that Microsoft’s state-of-the-art data centers may have consumed as much as 700,000 liters (184,920.45 gallons) of fresh water in this training.
Fortunately, startups like Crusoe are tackling this problem head-on. The startup recognizes that the world’s appetite for computation and energy will never stop growing. So they aim to pioneer a clean computing infrastructure by employing AI and deep learning to capture wasted energy.
Time will tell if the benefits of AI outweigh the costs, but meanwhile, we must continue developing energy-efficient AI algorithms and deploy innovations in the tech ecosystem to reduce the overall energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with AI models.
Data Quality and Availability Issues
Another major challenge in leveraging climate AI is the quality and availability of data. High-quality data is essential for developing accurate algorithms for predicting and addressing climate issues. However, obtaining reliable data on climate parameters can be difficult due to various reasons, such as the lack of standardized data collection methods, sparse geographical coverage, or inconsistency in measurement techniques. In some cases, data may be held by private organizations, limiting access for researchers and AI developers. These issues impede the AI models’ ability to provide precise predictions and actionable solutions for mitigating climate change.
Ethical and Social Considerations
Lastly, there are ethical and social considerations that need to be addressed when applying AI to climate change. The development of AI can exacerbate social and ethical challenges already associated with AI, such as privacy concerns, biases, and the potential misuse of technology.
For instance, the use of drones or other advanced technologies for monitoring or enforcing compliance with climate regulations may raise issues of trust and privacy. Additionally, the potential impacts on employment, income distribution, and social equity cannot be ignored when implementing AI-based solutions. To ensure the responsible and fair use of AI in combating climate change, it is important to address these ethical and social issues alongside technological advancements.

It’s Up to Us
The growing intersection between AI and the fight against climate change presents tremendous opportunities for innovation, but it also poses significant challenges that must be addressed before we invest too heavily in this technological solution.
While AI has the potential to provide valuable insights, optimize resource usage, and predict climate-related risks, its ecological footprint and the quality of available data are concerns. Additionally, ethical and social considerations must be taken into account. Striking a balance between leveraging AI’s potential and addressing its limitations is crucial. Continued research, innovation, and collaboration are needed to maximize the benefits of AI while mitigating its negative impacts.
The startups described above serve as prime examples of our uniquely human potential to creatively solve problems and drive the green tech revolution. While AI is a powerful tool that can assist us in tackling climate change, it is essential to recognize that it is ultimately human ingenuity, innovation, and collaboration that will pave the way forward.
As we harness the capabilities of AI and leverage its insights, we must remember that it is our collective responsibility to make informed decisions, address ethical considerations, and ensure the responsible use of technology. By combining the power of AI with our human drive for progress and sustainability, we can navigate the challenges of climate change and forge a brighter future for our planet.

